How Tramadol Works: Mechanism, Effects and Duration
Introduction
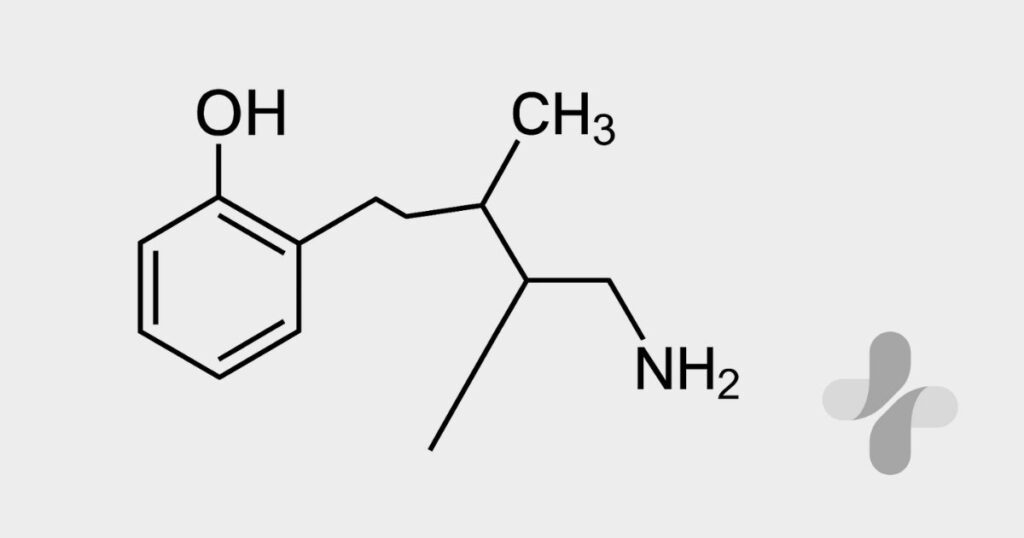
Tramadol is a commonly prescribed pain medication used for moderate to moderately severe pain, but its unique action in the body sets it apart from traditional opioids. Understanding how Tramadol works helps explain why it is effective for different types of pain and why it must be taken with caution. This guide explains its dual mechanism of action, onset time, duration, and the factors that influence how it behaves in the body.
How Tramadol Works in the Body
Tramadol has a dual mechanism, meaning it works through two distinct pathways to relieve pain. The first pathway involves weak stimulation of opioid receptors in the brain, which helps reduce the intensity of pain signals. Unlike stronger opioids, Tramadol binds more lightly to these receptors, which is why it is considered a milder opioid option.
The second pathway involves the inhibition of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. These two neurotransmitters play important roles in mood regulation and pain perception. By increasing their levels, Tramadol can amplify the body’s natural ability to control pain. This dual action makes Tramadol effective for both physical and nerve-related pain.
Therapeutic Effects of Tramadol
Because Tramadol targets pain through two different mechanisms, it offers several therapeutic benefits. It reduces the intensity of pain signals, making conditions such as chronic back pain, injury-related pain and postoperative discomfort more manageable. Its influence on serotonin and norepinephrine can also make it useful in cases where nerve pain is difficult to treat with standard pain medications. For some individuals, this dual action may improve comfort levels throughout the day and enhance overall functioning.
Onset of Action
Tramadol generally begins working within 30 to 60 minutes of taking an immediate-release tablet. This makes it suitable for short-term pain episodes or sudden flare-ups. Peak effects are typically reached around 2 to 3 hours after ingestion. Extended-release versions take longer to work but provide a steady level of pain relief over a 24-hour period, making them more appropriate for chronic or persistent pain.
Duration and Half-Life of Tramadol
Tramadol has an average half-life of 6 to 8 hours, though extended-release formulations last much longer. The half-life represents how long it takes for half of the medication to be processed by the body. Because of this duration, most immediate-release doses are taken every 4 to 6 hours depending on the level of pain. Extended-release products are designed for once-daily use, ensuring continuous pain control without frequent dosing.
Why Tramadol’s Dual Mechanism Matters
The dual action of Tramadol offers broader pain coverage than many standard analgesics, but it also introduces unique risks. Its opioid activity means it can cause sedation and carry a risk of dependence, while its impact on serotonin levels means it can interact with antidepressants and other medications that affect brain chemistry. Understanding this dual mechanism is important for recognising potential side effects and interactions.
Factors That Influence Tramadol’s Effects
Several factors can influence how Tramadol works in the body. Age is a major factor, as older adults may metabolise the medication more slowly, leading to stronger or longer-lasting effects. Kidney and liver function also play a significant role because the body processes Tramadol through these organs. Other medications—especially antidepressants, sedatives and alcohol—can intensify its effects or increase the risk of side effects such as serotonin syndrome or respiratory depression.
Importance of Using Tramadol Safely
Because of its dual mechanism, Tramadol must be used carefully. Combining it with alcohol, benzodiazepines or other sedatives can lead to dangerous levels of drowsiness or breathing difficulties. Its influence on serotonin and norepinephrine also means it should not be combined with certain antidepressants without medical approval. Understanding how the medication behaves in the body helps ensure safer use and reduces the chances of unwanted complications.
Summary
Tramadol works through a unique dual mechanism, stimulating opioid receptors while also increasing serotonin and norepinephrine levels. This combination provides effective pain relief for a wide range of conditions, from injury-related discomfort to chronic nerve pain. Its onset is relatively quick, and its duration makes it suitable for both short-term and long-term pain management. However, because of its potential interactions and dependence risks, Tramadol must always be used under medical guidance to ensure safe and effective treatment.